Great sleep is a pillar of health. Restful sleep boosts our energy levels, sharpens our focus, and enhances our wellness. Unfortunately, most of us don’t sleep enough. And sleep disturbances keep millions of people tossing and turning every night.
Here are 28 science-backed strategies to upgrade your life through better sleep.
1) Take A Bath
A warm bath or shower will make you fall asleep faster. The body’s core temperature naturally cools at night. So you sleep better when your body stays cool.

Paradoxically, soaking in warm water increases blood flow (and heat) to your skin, cooling your core temperature. Take a warm bath or shower 1-2 hours before bed to fall asleep faster and sleep better (Haghayegh 2019)
Read more about the health benefits of bathing in this article:
Take a Bath to Recover Faster?
2) Check Your Mattress
Great sleep starts with a quality mattress. As mattresses get older, they soften and provide less support for your body. Sleeping on an old, saggy mattress is not ideal for your spine or your sleep quality.
Here are 3 signs you might have a bad mattress:
- Your mattress is older than your teenage son
- You sleep better on the couch
- The mattress is u-shaped so you always end up in the middle of the bed

Generally, firmer mattresses support the spine better. But everyone’s different. Some people wake up feeling limber after sleeping on a soft mattress. The key is finding the right mattress for you.
Personally, I recommend the Tuft & Needle mattress. I have slept well on T&N beds for the past 6 years.
A Tuft & Needle mattress is breathable, supportive, and moderately firm. Plus, you can try it for 100 nights and send it back if you don’t like it. If you’re looking for a new mattress (or should be), give this one a look: See it on Amazon here.
Bottom line: It’s tough to sleep well without a good mattress. Consider a new mattress an investment in your health. Better sleep will enhance every area of your life.
3) Protect Your Bed
Your brain associates physical spaces with specific activities. For example, your brain is used to thinking hard at your desk. Or gobbling down ice cream after visiting the freezer. (At least that’s how my brain works.)
So limit your activities in bed. You want your brain to associate your bed with rest and relaxation – not work, stress, social media or TV. Reserve your bed for sleep and intimacy with your partner.
Protect your bed for better sleep.
4) Exercise
Exercise gives you more energy and improves your sleep. I’m not saying you should run sprints right before bedtime after chugging 3 Red Bulls. (We’ll cover caffeine in tip #22)
You’ve probably experienced this firsthand–whether it’s yard work, moving boxes, or exercising hard for hours on end–it’s effortless to fall asleep after a physically demanding day.

Exercise will make you more sleepy. Plus, it reduces sleep issues like insomnia, sleep apnea and restless leg syndrome (Amiri 2021).
If you’re looking to start an exercise routine, try one of these 7 low-impact cardio exercises.
5) Aim for 8
Sleeping too little is linked to a host of health problems. Most adults need 7-9 hours of sleep every night to feel rested. You can’t operate at 100% without adequate sleep.
Sufficient sleep has countless health benefits. For example, it boosts your immune system, strengthens your memory, sharpens your focus. Extra sleep even boosts athletic performance (Mah 2011).
6) Fuel Right
Avoid massive meals before bed. That way, reflux doesn’t keep you awake and uncomfortable.
Ideally, you want to go to bed satiated, but not too full. Scientists believe several specific foods can enhance sleep. Cherries can help you fall asleep faster. And food containing tryptophan (like milk and turkey) boosts sleep quality (Binks 2020).
7) Eu-Hydrate
Euhydration is the state of ideal hydration – You aren’t dehydrated, but you aren’t getting out of bed to use the bathroom every 20 minutes, either.
Dehydration has well-known downsides. It causes problems like dizziness, low blood pressure and lethargy.

But overhydration can pose a threat to your health (and your sleep), too. Drinking too much water will make you wake up frequently throughout the night.
And severe overhydration can cause electrolyte imbalance, hyponatremia and even death. Stay hydrated, but not too hydrated, to sleep better and be safer if you wake to use the bathroom at night.
8) Keep it Cool
Your body’s core temperature falls a few degrees as night approaches, coinciding with the sleep-inducing release of melatonin. A cool sleep environment is key to great sleep.
Set the thermostat to 60-67 degrees Fahrenheit (15.6-19.4 degrees Celsius) for a great night’s sleep.
9) Set the Mood
Turn off bright lights (and bright screens) 1-2 hours before bed. Bright light wakes up your brain.

And dim light tells your brain to prepare for sleep. So create a soothing environment with soft lights to prepare your body to sleep.
10) Black Out
No, drinking alcohol until you pass out won’t help you sleep better. (Scroll down to #26 to learn how alcohol affects sleep.)
Blackout curtains are a different story. Here’s why they work:
Blackout curtains keep light pollution out of your bedroom. Without light-blocking curtains, outdoor lights brighten your bedroom and tell your brain to stay awake.
When I hung up blackout curtains, my sleep quality skyrocketed. So if light pollution is keeping your bedroom right, pick up Amazon’s best blackout curtains.
The darker the bedroom, the deeper the sleep.
11) Mask On
Your eyes absorb a lot of light. Light can get through your lids – just think of when you forgot your sunglasses at the beach. It’s still bright to look into the sun, even when you’re squinting or closing your eyes.

Pick up a sleep mask (this is the one I use) to darken a bright room. It’s clutch for traveling when the room isn’t completely dark – and there’s not enough luggage space to bring blackout curtains!
12) Be Boring
Your brain likes habits. It saves decision-making energy and promotes efficiency. A predictable sleep schedule it’s key to quality sleep.
It’s not fun, exciting, or complicated. But going to bed and waking up at the same time every day (within 1 hour) is a simple way to sleep better.
13) Bedtime Routine
My newborn son sleeps well after his bedtime routine. My wife and I go for a walk around the neighborhood, give him a bath, feed him and then put him to bed.
His brain and body have grown accustomed to the bedtime routine. So he falls asleep like clockwork at 8PM.
There’s still a baby in all of us. We crave consistency before bed. Find a few relaxing activities to do every night before bed.
14) Breathe Deep
Deep breathing turns on the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for rest and relaxation. It also turns down the opposite system, the sympathetic nervous system, which jolts the body into “fight or flight” mode.

Whether you prefer yoga, guided meditation, or just taking a few deep breaths, carve out a few minutes to calm down your sympathetic nervous system before bed.
15) Cuddle
Pet your dog, hug your child, or cuddle with your partner.

These activities release oxytocin, the “love hormone” that creates feelings of connectedness, relaxation and well-being. An oxytocin boost before bed makes it easier to drift off into a peaceful sleep.
16) Sleep at Night
Unless you have to work the night shift, sleep at night. Night shift screws up the body’s internal clock. Overnight shift work is linked to chronic health problems like heart disease, stroke and obesity.
The human body is designed to sleep at night. Staying up too late or working the night shift disrupts circadian rhythms and causes a host of health problems.
So unless you have to work the night shift (or live at the North Pole), sleep when it’s dark and wake up when it’s light outside.
17) Align Your Spine
First of all, your spine can’t go out of alignment. At least not without a massive trauma. That is one of the top 10 back pain myths.
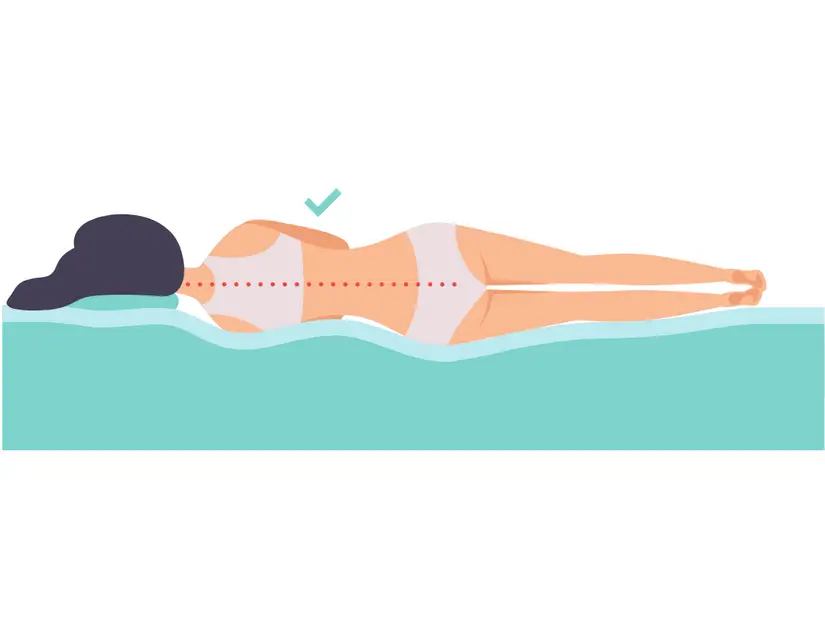
By “align your spine,” I mean keeping your spine in a neutral position. Aim for a straight line from your neck to your ankles. Use towels and pillows to accommodate your body’s natural curves, as described in this article.
18) Support Your Neck
We’ve all been there: you forget your pillow. And the hotel pillows are either too thin, too thick or too fluffy. In the morning, you wake up with neck pain from sleeping wrong.
Proper cervical spine support is especially important for side sleepers. Anecdotally, that’s about 80% of my clients. Try my folded towel hack to give your neck better support at night.

19) Find the Right Pillow
Pillows are very individual. Your favorite pillow may make my neck stiff for a month. And vice versa.

Many side sleepers like the Weekender pillow, rated 4.3 stars on Amazon. My wife loves her Weekender pillow. Check it out here.
I’m a stomach sleeper so I prefer a thinner, less supportive pillow.
Back sleepers like pillows that are somewhere in the middle – not too big, not too small.
Bottom line: comfort is king. Your body is smart and will tell you what feels comfortable.
The more comfortable your pillow, the better you will sleep. If you find yourself sleeping too hot, get a cooling pillow to feel like your head is always on the best side of the pillow.
20) Limit Blue Light at Night
Blue light, commonly emitted by phones, TVs, computers and other screens, tells our brain to wake up. It blocks melatonin release (Tahkamo 2018). And that’s a problem at bedtime.
Fortunately, there are a few easy ways to limit blue light before bed. First, turn off the TV and computer a couple hours before bedtime. Second, dim your computer, tablet and phone screens. Finally, you can pick up a pair of blue-light blocking glasses.
These glasses are proven to reduce insomnia and increase focus at work.
21) The Sunshine State
Use light to your advantage in the morning. Getting into the morning sunshine reinforces your circadian rhythm, telling your brain to wake up.
So go outside, or at least under some bright lights, early in your day. You can even “rise with the sun” in your blacked-out bedroom with a sunshine alarm clock.
22) Consciously Caffeinate
Caffeine is one of the 3 best fitness supplements. However, it impairs sleep when it’s taken at the wrong time or in excess.
Some guidelines recommend stopping all caffeine intake after a certain time, like lunchtime, 2PM, or 4PM. But caffeine’s effects vary based on variables like the dose (1 cup of coffee vs. a quad espresso) and your caffeine tolerance.
Here’s how caffeine works:
Caffeine blocks chemical reactions in your brain that make you sleepy.
Normally, adenosine builds up and binds to its receptors throughout the day. And when adenosine binds to its receptors, you feel tired. It’s a built-in system to make you sleepy when it’s bedtime.
However, caffeine also binds to adenosine receptors, blocking adenosine from attaching to its receptors. That’s how caffeine fights fatigue and keeps you awake, whether you like it or not.

Caffeine has a half-life of about 6 hours, meaning 100mg caffeine (1 cup of coffee) at 6AM turns into about 50mg caffeine in your bloodstream by noon. It stays in your body long after you drank that afternoon cup of joe or delicious pre-workout beverage.
Caffeine shows up in many food and drink products like soda, coffee, tea, chocolate and energy bars. Take a close look at your nutrition to ensure that caffeine isn’t keeping you up at night.
If caffeine has you tossing and turning in bed, caffeinating wisely is a simple solution for better sleep.
23) Turn Off The News
If you’re still reading, you must be serious about getting better sleep. I saved the best (and most controversial) tips for last. Turning off the news is one of my 3 unpopular sleep tips.
The (mostly negative) news turns up the sympathetic nervous system, activating the “fight or flight” response. The sympathetic nervous system plays tug-of-war with the parasympathetic system, regulating the body’s alertness and arousal.
The sympathetic nervous system says “go to war” while the parasympathetic system says “go to sleep.” Both systems play key roles. And the parasympathetic system takes center stage when it’s time to sleep.
Not only does the news amp up your sympathetic nervous system, the blue light from the TV isn’t helping your sleep.
The human brain isn’t designed to process the worst and scariest happenings in the world of billions of people. When I stopped watching the news on a regular basis, my stress levels plummeted and I felt happier.
Try turning off the news before bed and see if you sleep better.
24) Unplug
“Do not disturb” is your best friend at night. Keep your phone, watch, tablet and other devices silent.

And turn off email and social media notifications until morning. Hearing (or expecting) alerts will keep your brain active all night long and prevent deep, restful sleep.
Plus, blue light from devices suppresses melatonin production, making sleep elusive.
25) Move Your Phone
On the same note, keeping your phone next to your bed isn’t doing your sleep any favors. Sleep is when our mind and body need to unplug from technology, rest and recover.
Try sleeping with your phone out of the room, or at least several feet out of reach.
You’re less likely to doom-scroll through Twitter if you can’t fall asleep. And you won’t check texts, email and social media throughout the night.
26) Cut the Booze
Alcohol makes it easier to fall asleep. But there’s a price to pay.

Booze disrupts the rapid eye movement (REM) phase of sleep (Colrain 2018). It also makes you sleep hotter. Ultimately, it causes lower quality sleep and more fatigue the next day.
On average, the human body processes one drink per hour. Experts recommend going to sleep after your body processes the booze.
27) Beware of Sleeping Pills
Much like alcohol, many sleeping pills disrupt REM sleep and make you groggy. If you’re curious, ask your medical doctor or pharmacist about sleep medications for your specific situation.
28) Don’t Sweat It
Individually, each of these recommendations can enhance your sleep. But don’t try them all at once.

Trying too hard to sleep well makes it harder to rest. Like how it’s harder to make a free throw, or fall in love, or tie your shoes fast when you try too hard.
Implement changes gradually and use as few sleep aids, tips and hacks as possible to get great sleep.
Read More
For an easy-read sleep guide with quick, practical applications, check out the book Sleep Smarter by Shawn Stevenson.
For an in-depth, scientific exploration of sleep from a certified sleep expert, pick up Why We Sleep by Dr. Matthew Walker.
Readers: How do you sleep at night? What improves your sleep? What makes it worse? Did any of these tips surprise you? And which ones do you plan to try? Share your thoughts in the comments.
For more evidence-based insights to live a healthier life, join the free, fast-growing Facts & Physio Newsletter. Plus, get The Recovery Checklist when you sign up.

